NER und Sentiment-Pipeline mit Services zur Datenextraktion. --------- Co-authored-by: Philipp Horstenkamp <philipp@horstenkamp.de> Co-authored-by: TrisNol <tristan.nolde@yahoo.de>
20 KiB
DevOps for the Transparenzregister analysis¶
Dependency management in Python¶
Tools¶
The requirements.txtlists all the dependencies of a project with version number and optionally with hashes and additional indexes and conditions for system specific differences.- Changes are difficult because auf interdependency.
- Sync with requirements.txt is impossible via pip.
- All indirekt requirements need to be changed manually.
- Security and other routine upgrades for bugfixes are annoying and difficult to solve.
- Adding new requirements is complex.
pip-toolsis the next level up.- Generates
requirements.txtfromrequirements.ini - Allows for sync with ``requirements.txt`
- No solution to manage multiple combinations of requirements for multiple problems.
- Applications or packages with dev and build tools
- Applications or packages with test and lint tools
- packages with additional typing packages
- A combination there of
- Generates
pip-compile-multiis an extension ofpip-toolsand allows for the generation of multiple requirements files.- Only configured combinations of dependency groups are allowed.
- Different configurations may find different solutions.
poetryis the most advanced tool to solve python dependencies- Comparable to Javas
maven - Finds a complete solution for all requirement groups and installed groups as defined
- Allows for upgradable packages in defined bounds.
- Exports a solution that can be used on multiple machines to guarantee the same environment
- Handling of Virtual environments
- Automatically includes requirements in metadata and other entries for wheel when building
- Build and publication management
- Complete packaging configuration in
pyproject.tomlas required in PEP 621 - Supports plugins
- Comparable to Javas
Defined Poetry dependency groups in our project¶
| Group | Contents & Purpose |
|---|---|
| root | The packages needed for the package itself |
| develop | Packages needed to support the development such as jupyter |
| lint | Packages needed for linting such as mypy, pandas-stubs & ruff |
| test | Packages needed for testing such as pytest |
| doc | Packages needed for the documentation build such as sphinx |
How to use poetry¶
poetry new <project-name>command creates a new poject with folder structure and everything.poetry initadds a poetry configuration to an existing project.poetry installIf the project is already configured will install the dependencies.- kwarg
--with devforce it to install the dependencies to develop with. In our case that would be a jupyter setup. - kwarg
--without lint,testforces poetry to not install the dependencies for the groups lint and test. For our case that would include pytest, mypy and typing packages.
- kwarg
poetry add pandas_typing<=2would add pandas with a versions smaller than2.0.0as a dependency.- kwarg
--group lintwould configure it as part of the dependency group typing. - A package can be part of multiple groups.
- By default, it is part of the package requirements that are part of the requirements if a build wheel is installed.
- Only direct requirements are configured! Indirect requirements are solved.
- kwarg
poetry updateupdates the dependency solution and syncs the new dependencies.- Requirement files can be exported.
The full documentation can be found here!
Linter¶
Python is an
- interpreted
- weak typed
programing language. Without validation of types and other compile mechanisms that highlight some errors.
Lint stands for lint is not a software testing tool and analyses the code for known patterns that can lead to different kinds of problems.
Why lint: Application perspective:¶
- In Compiled programming languages many errors a thrown when a software is build. This is a first minimum quality gate for code.
- Hard typing also enforces a certain explicit expectation on arguments are expected. This is a secondary quality gate for code python does not share.
- This allows for a certain flexibility but allows for careless mistakes.
- Helps to find inconsistencies
- Helps to find security vulnerabilities
Why lint: Human perspective:¶
- Certainty that naming conventions are followed allows for an easier code understanding.
- Auto whitespace formatting (Black)
- Absolut whitespace formatting allows for a clean differentials when versioning with git.
- The brain does not need to adapt on how somebody else formats his code
- No time wasted on beatification of code through whitespace
- Classic linter
- Faster increas in abilities
- Nobody needs to read a long styleguide
- Reminds the programmer of style rules when they are violated
- Contributers from otside the project can contribute easier
- Code simplifications are pointed out
- Reduces the number of variances for the same functionality
Collection of Recommended linter¶
- Black for an automatic and absolut whitespace formatting. (No configuration options)
- Ruff faster rust implementation of many commonly used linters.
- Reimplementation of the following tools:
- flake8 (Classic python linter, unused imports, pep8)
- isort Automatic import sorting (Vanilla python, third party, your package)
- bandit (Static code analysis for security problems)
- pylint (General static code analysis)
- many more
- Fixes many things that have
simplefixes - Relatively new
- Endorsed from project like pandas, FastAPI, Hugging Face, SciPy
- Reimplementation of the following tools:
- mypy
- Checks typing for python
- Commonly used linter for typing
- Often needs support of typing tools
- Sometimes additional typing information is needed from packages such as
pandas_stubs.
- pip-audit checks dependencies against vulnarability db
- pip-license checks if a dependency has an allowed license
Testing with Pytest¶
Even tough python comes with its own testing framework a much more lightweight and more commonly used testing framework is pytest
tests/basic_test.py
from ... import add
def test_addition():
assert add(4, 3) == 7, "The addtion did not result into the correct result"
Parametizeed Test¶
In addition, pytest contains the functionality to parameter its inputs
tests/parametriesed_test.py
import pytest
from ... import add
@pytest.mark.parametize("inputvalues,output_value", [[(1,2,3), 6], [(21, 21), 42]])
def test_addition(inputvalues: tuple[float, ...], output_value: [float]):
assert add(*inputvalues) == output_value
Tests with setup and teardown¶
Setting up an enviroment and cleaning it up afterwords is possible with pytest's fixture
tests/setup_and_teardown_test.py
import pytest
from sqlalchemy.orm import Session
@pytest.fixture()
def create_test_sql() -> Generator[Session, None, None]:
# create_test_sql_table
# create sql connection
yield sql_session
# delete sql connection
# delete sql tables
def test_sql_table(create_test_sql) -> None:
assert sql_engine.query(HelloWorldTable).get("hello") == "world"
Tests are run with the following command
poetry run pytest tests/
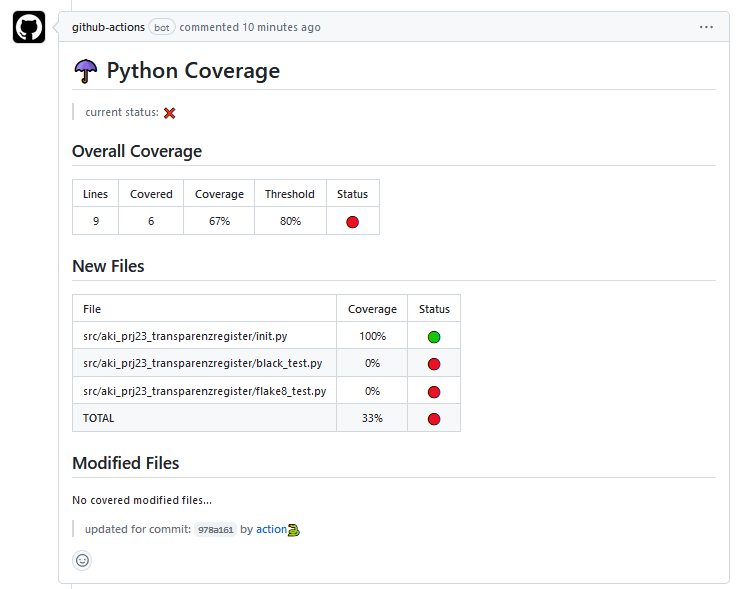
Code Coverage¶
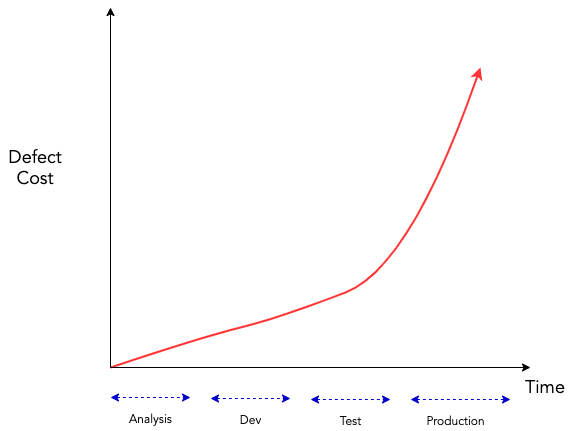
Code coverage reports count how many times a line was executed and therfore tested.
They can eiter be integrated into an IDE for higliting of missing code or reviewed directly.
Either over third party software or by the html version that can be found with the build artifacts.
pre-commits¶
Git is a filesystem based versioning application. That includes parts of its code are accessible and ment to be manipulated. At different times of the application a manipulate script can be executed. Typicle moments are on:
- pull
- push / push received
- pre-commit / pre-merge / pre-rebase
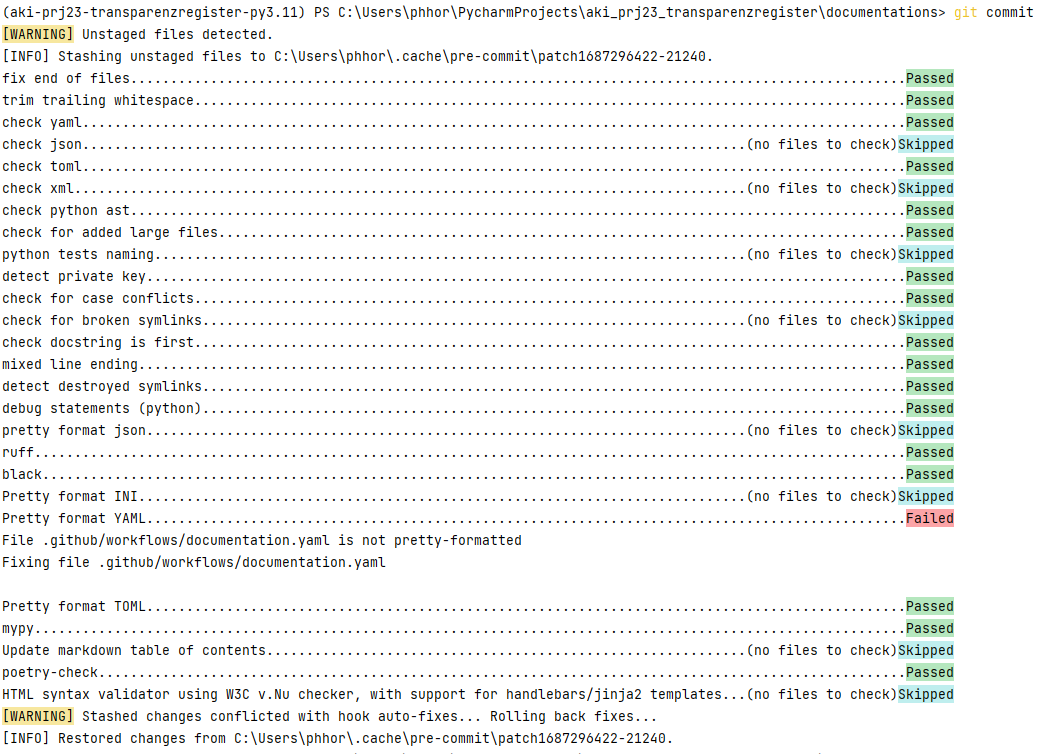
The pre-commit package hooks into the commit and implements a set of programms before committing
Files can be edited or validated
pre-commit execute fast tests on changed files to ensure quality of code.
Bohems Law
Since they are executed on commit on only the newly committed files a response is much faster. The normally only include linting and format validation tools no testing. Sometimes autofixer such as black, isort and ruff.
Configured pre-commit hooks:
- format checker + pretty formatter (xml,json,ini,yaml,toml)
- secret checker => No passwords or private keys
- file naming convention checker for tests
- syntax checker
- ruff => Linter
- black => Whitespace formatter
- poetry checker
- mypy => typing checker
- md-toc => Adds a table oc contents to an *.md where
<!--TOC-->is placed
Pre commits are installed with the command
pre-commit install
The pre commits after that executed on each commit.
If the pre-commits need to be skipped the -n option skips them on commit.
Documentation build with sphinx¶
There is no single way to use to build a python documentation. Sphinx is a commonly used libarary.
- Builds a package documentation from code
- Native in rest
- Capable of importing *.md, *.ipynb
- Commonly used read the docs theme
- Allows links to third party documentations via inter-sphinx (pandas, numpy, etc.)
Currently implemented to build a documentation on pull_requests and the main branch.
Automatically deployed from the main branch.
GitHub¶
GitHub is a central hub for git repositories to be stored and manged.
In addition, it hosts project management tools and devops tools for:
- testing
- linting
- analysing
- building
- deploying code
Example GitHub action workflow¶
Workflows are defined in .github/workflows/some-workflow.yaml
name: Build
on: # when to run the action
pull_request:
A single action of a workflow.
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest # on what kind of runner to run an action
steps:
- uses: actions/setup-python@v4 # setup python
with:
python-version: 3.11
- uses: snok/install-poetry@v1 # setup poetry
with:
version: 1.6.1
virtualenvs-path: ~/local/share/virtualenvs
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- run: |
poetry install --without develop,doc,lint,test
poetry build
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
with:
name: builds
path: dist/
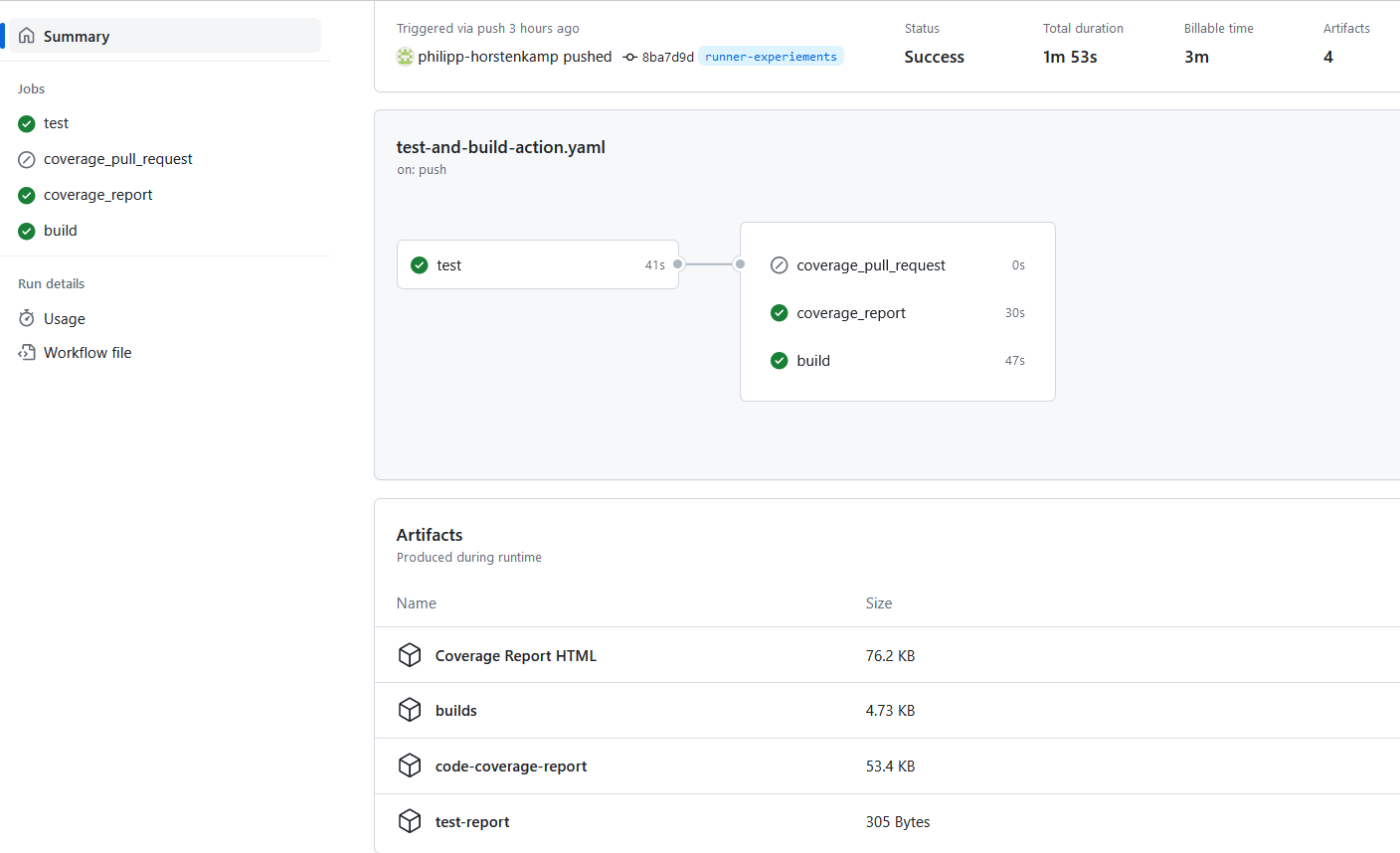
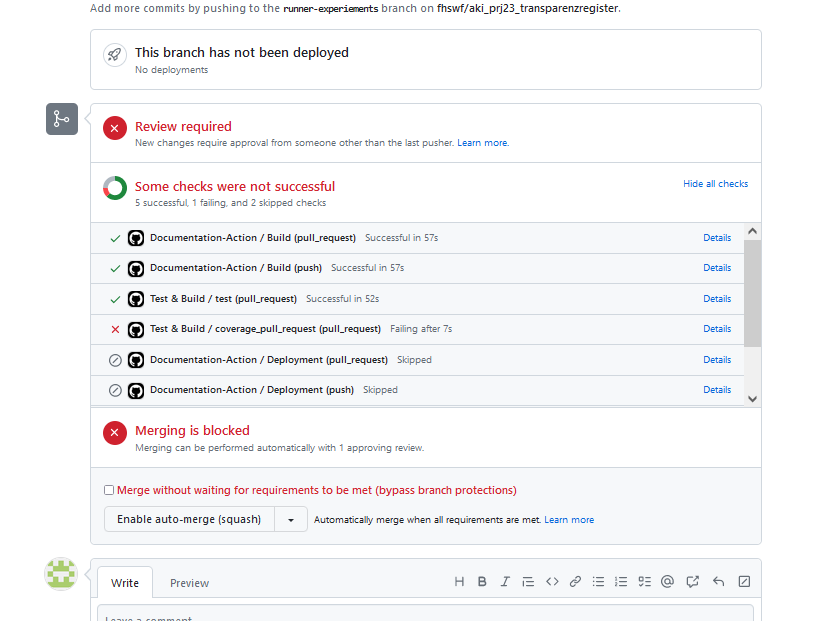
Test and Build-pipeline with GitHub actions¶
On push and pull request:
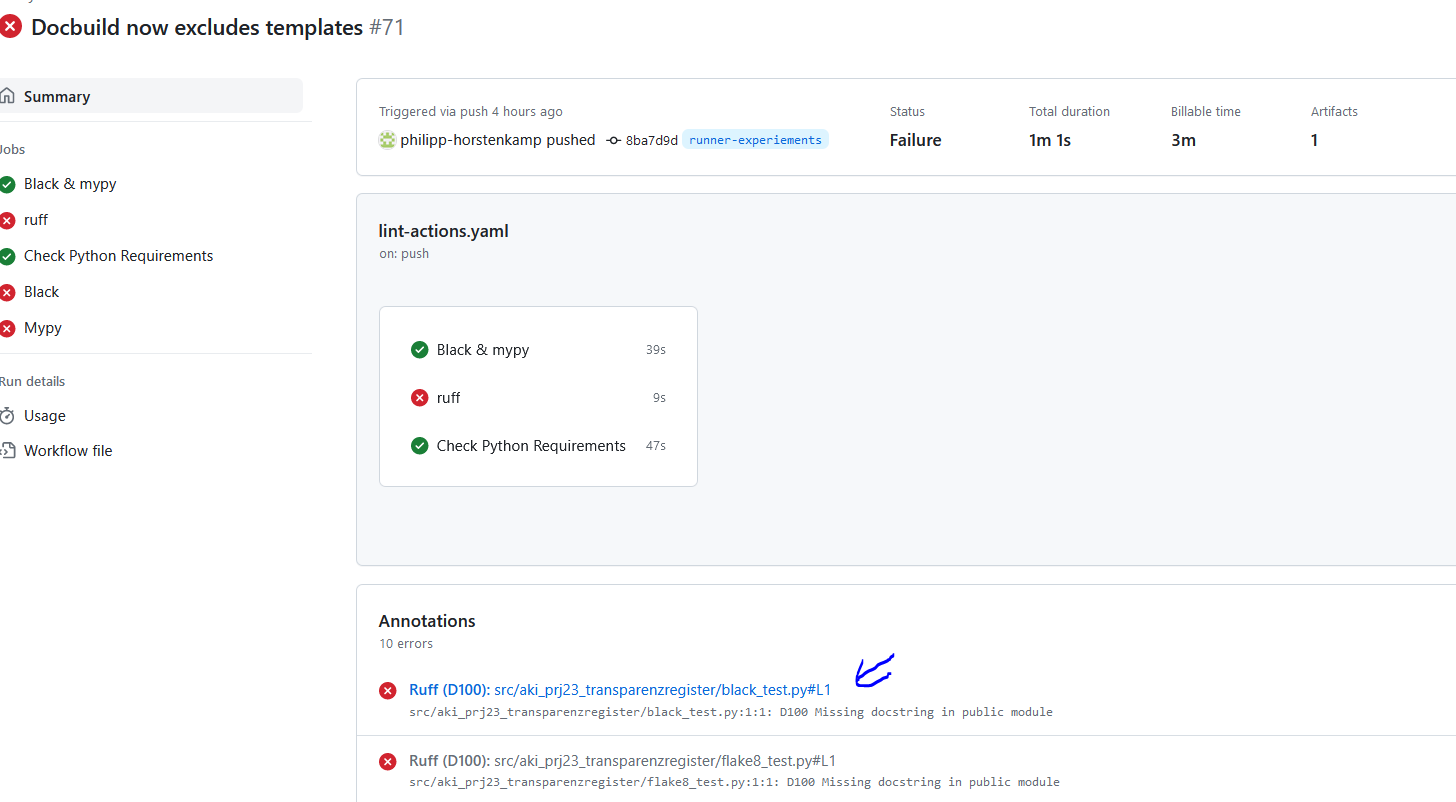
- Lint + license check + dependency security audit
- Problem summaries in GitHub actions + Problem notification via mail
- Test with pytest + coverage reports + coverage comment on pull request
- Python Build
- Documentation Build
- Documentation deployment to GitHub pages (on push to main)
On Tag:
- Push: Docker architecture and CD context still unclear
Build artifacts¶
- Dependencies / versions and licenses
- Security report
- Unit test reports and coverage report as
.coverage/coverage.xml/html! - Build wheel
- Build documentation
- probably. one or more container
- if needed documentation as pdf
Dependabot¶
Dependabot is a GitHub tool to refresh dependencies if newer ones come available or if the currently used ones develop security flaws. Dependabot is currently not python compatible. Dependabot is a tool for a passive maintenance of a project without the need for much human overside.
GitHub Runner Configuration and what does not work¶
Most GitHub actions for python reley on the actions/python-setup action.
This action is not available for linux arm.
Workarounds with a python docker container / an installation of python on the runner and other tools do not work well.